Virtual reality training leverages immersive technology to place trainees inside a simulated environment transporting them to another time, place or situation.
These kinds of simulations give users the ability to experience and interact with the virtual world around them. When properly designed, users believe what they are seeing and doing is actually real. VR coaching can lead to reduced training times, better knowledge retention, and overall improvement in job performance.
Virtual practice simulations are also a great option for companies that are looking to provide training remotely or at scale. Most VR systems no longer require external computers or sensor arrays, making the setup and shipping of these systems much simpler than in the past.
In addition, with nothing more than a standard WiFi connection, instructors can monitor trainee progress and interact with the simulations in real-time from anywhere on the globe. There are also a number of software solutions available for robust tracking and monitoring of trainees, similar to traditional learning management systems.
There are two types of instruction that work particularly well in virtual simulations:
- Technical skills training
- Soft skills training
Technical Skill Training
Technical simulations are most commonly used to immerse trainees in situations that would otherwise be too difficult, too dangerous or too expensive to recreate in the real world.
Immersive technical training allows users to walk around and interact with their environment in a completely safe and controlled manner. VR technical training has proven to be a valuable tool for practicing multi-step or complex tasks, learning new pieces of complicated machinery, mastering control interfaces, practicing skills in differing conditions and more.
Here’s a real-world example: JLG, an industry leader in commercial lifts and loading equipment, recently turned to the power of VR training to provide a more efficient way for their customers to train new recruits. The company added value to their own product offerings while also helping solve a customer pain point.
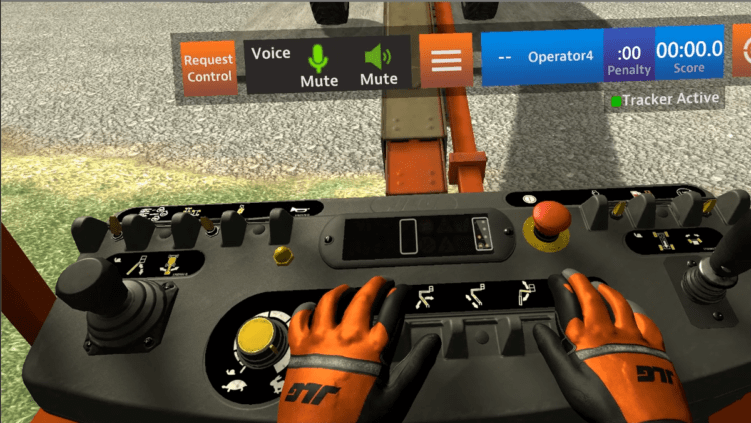
Photo Credit: JLG
Soft Skills Training
Scenario-based learning also allows users to participate in situations that would otherwise be too difficult, too dangerous or too expensive to replicate in the real world. Differing from technical VR training, however, these simulations allow trainees to experience things from the perspective of someone else. They can also force users to make critical decisions under pressure. This type of VR training is proving itself to be a valuable tool that can help improve interpersonal skills, complete compliance requirements, build leadership expertise or tackle sensitive HR-related topics.
A 2018 study by Stanford University shows that VR soft skills training can be highly effective at building compassion and empathy when compared to traditional training methods.
Why VR Training
Simply put, VR training is effective because it tricks the user’s brain into believing that what they’re experiencing is real.
In technical training scenarios, users go through physical motions, building muscle memory and firing the same neuroreceptors in the brain as if the person were actually performing the task in the real world.
And because soft skills training gives users the opportunity to see things from a different perspective, it employs a sense of presence for the trainee that creates an emotional connection. The training scenario becomes a personal experience for the trainee, which can lead to a long-lasting mental impression of the moment and, in turn, create deep-seated memories within the user’s brain.
When looked at through a scientific lens, both technical and soft skills VR training create activity in the user’s brain that is indistinguishable from actually taking part in the task in the real world. It has also been found that employees tend to find VR training more enjoyable when compared to traditional training methods.
Digital Environments For VR Training
Digital environments — created inside of a computer program — present a nearly unlimited ability to design simulations that offer complete interactive freedom. Because of this, most technical VR training is designed using digital simulation. This technology also allows for real-time adjustment of scenario variables, increasing or decreasing the level of difficulty and multi-user experiences.
As an example, UPS has been leveraging digital VR training to help educate new drivers since 2017. In these simulations, instructors can change weather and road conditions as well as the behavior of delivery trucks in real time, depending on a new driver’s ability and points for improvement.
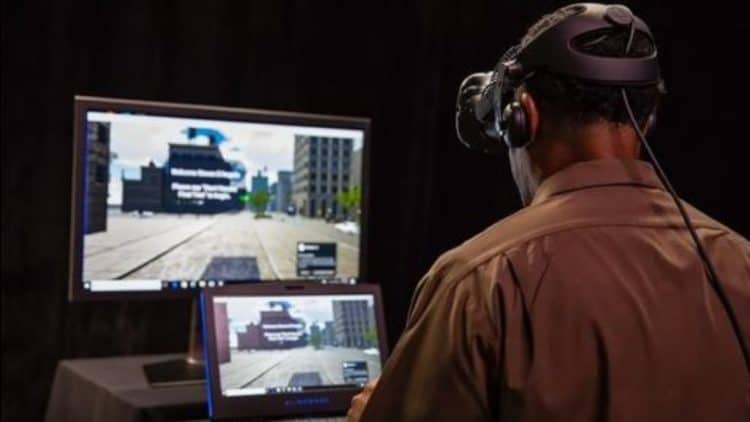

Photo Credit: VRScout
However, digital simulations can create challenges in certain learning scenarios due to the “uncanny valley”: the unsettling feeling we get from robots and virtual agents that are too human-like. Training topics that require a higher level of intimate or emotional connection can be difficult to execute when leveraging digital simulations. Using this type of environment for more intimate training scenarios can lead to disconnectedness, and in cases like these, using 360-degree video can be a powerful alternative option.
360 Video For VR Training
Most commonly used in soft skills training, 360-degree video tends to eliminate problems arising around the uncanny valley. Because these simulations are designed and built using actual captured video and real human actors, the emotional connection to characters in this type of training simulation is more easily maintained. However, compared to digital simulations, these 360-degree VR experiences are inherently more limited in terms of interactivity and real-time adjustability. Video-based immersive training tends to be a better tool for experiences that focus on emotional, human-centered or empathy-based training scenarios.
Western State Hospital, the largest psychiatric in-patient facility west of the Mississippi, recently completed a 360-degree video training program that gave trainees the ability to experience the symptoms of severe mental illness from the perspective of a patient. “I’ve heard people say they hear voices, but I’ve never seen something make it so real,” said Terry Stevenson, a registered nurse at the hospital, after going through the VR training program. “I think this will help me when I’m talking to somebody and they’re not responding.
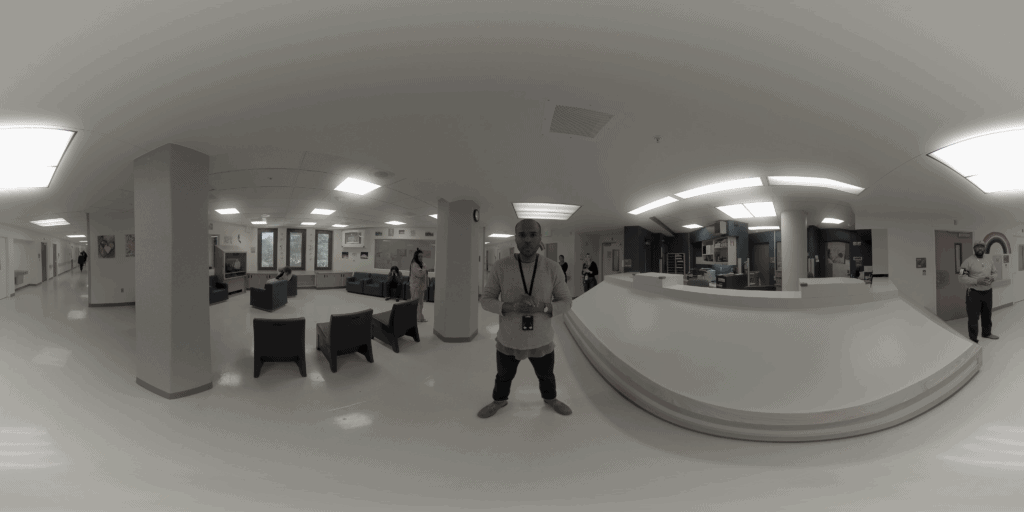

Photo Credit: CM&D
Proven Results
When designed following industry best practices, VR training simulations are proving their value in the real world. A recent study by PWC showed VR learners were up to four times faster at retaining new information and 275 percent more confident to act on their new skills when compared to traditional in-classroom instruction. Since making VR a part of their new driver training program, UPS has seen information retention rates increase by as much as 75 percent. And Walmart has seen academic test scores improve by 10 to 15 percent when students use 360-degree VR during training.
Things to consider
First-time investments in VR training can be daunting. These experiences can seem expensive at the beginning, and it is not uncommon to find challenges around budget approval and buy-in from leadership. VR is still relatively new, and there is also a fair amount of hype-fatigue hanging around from the technology’s overpromised reemergence in early 2010s.
But things have changed. VR technology has improved dramatically in just the last few years, and there are countless business and scientific case studies that prove the value this technology can offer as a training tool. When implemented according to the industry’s best practices, VR training for both technical and soft skills can lead to impressive results compared to traditional training methods.
Today, there is a robust VR training industry taking shape around the world, including many great firms right here in Texas. Are you ready to take your organization’s training to the next level!?
This article has been cross-posted on BuiltIn.com as part of their Expert Contributors network: How VR Training Can Supercharge Your Employees Skills


